Merostomata (Merostomates)
Merostomata is the name given to a grouping of the extinct Eurypterida (sea scorpions) and the Xiphosura (horseshoe crabs). The term was originally used by James Dwight Dana to refer to Xiphosura only, but was emended by Henry Woodward to cover both groups.
The name "Merostomata" derives from the Greek roots μηρός (meros, "thigh") and στόμα (stoma, "mouth"), in reference to the animals possession of appendages which are mouthparts at their proximal end, but swimming legs at their distal end.
The scientific consensus at the beginning of the twentieth century was that these two marine groups were closely related, and only more distantly related to the terrestrial Arachnida.More recent analyses suggest that the grouping Merostomata is not monophyletic, with Xiphosura being basal to a clade comprising Eurypterida and Arachnida.[3] It is estimated that the Xiphosura diverged from the Arachnida 480 million years ago.The shared features of the two groups traditionally grouped in the Merostomata are now thought to be retentions of primitive conditions (symplesiomorphies), and thus it has been recommended that the name Merostomata be abandoned.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Merostomata
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Virtual museum of the Czech Geological Survey, www.geology.cz, (C) Czech Geological Survey, 2011, v.0.99 [13.12.2011]
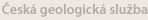

![[ENG]](img/vlajka-cr.gif) Česky
Česky 

 Previous
Previous