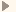
Rhynchonelliformea (Rhynchonelliforms)
Rhynchonelliformea is the name now given to the articulate brachiopods, Class Articulata, revised as a subphylum. Articulate brachiopods are those with hard, articulated, shells (hense the term) with a simple set of opening and closing muscles. The name, Rhynchoelliformea, which replaces Articulata, which is also a class of crinoids, comes from the family Rhynchonellidae, which however is no more representative of articulate brachiopods that any other group such as spirifers or strophomenids. It just happens to be the name chosen, based on an included taxon.
The main difference between the Rhynchonelliformea described in the Treatise Part H, revised 2000/2007, and the Articulata of the Treatise part H, 1965, lies in the groups included, their taxonomic positions and arrangements. The Rhynchonelliformea (Articulata revised) is divided into five classes: Obolellata, Kutorginata, Chileata, Strophomenata, and Rhynchonellata. The Strophomenata and Rhynchonellata are found living today; the Rhynchellata as the major constituent of modern brachiopod faunas, the Stromphomenata as only a minor contributor. The Obolellata, Kutorginata, and Chileata are all extinct. The Obolellata and Kutorginata are restricted to the Cambrian, the Chileata ranges throughout the extent of the Paleozoic. In the older classification of the Treatise (1965) the Class Articulata was divided into six orders, the Orthida, Pentamerida, Rhynchonellida, Spiriferida, Terebratulida, and Strophomenida. The Orthida, Pentamerida, Rhynchonellida, Spiriferida, and Terebratulida became combined as the Rhynchonellata. The Strophomenida became the Strophomenata with the addition of the Orthotetida and Billingsellida and separation of the Chileata. The Obolellata and Kutorginata were previously included in the Inarticulata, but have since been recognized as primitive articulates. One of the more significant changes in the new classification is the splitting of the original Spiriferida into distinct and separate orders, the Spiriferida as revised, Atrypida, Athyridida, and Spiriferinida; each with its own derivation and phylogeny. Originally these were included as suborders within the Spiriferida which combined brachiopods with spiral (coiled spring-like) brachidia regardless of the orientation or the length of the hinge line or whether the shell was impunctate or punctate. The newer classification recognises the spiral brachidia being a matter of evolutionaly convergence. The Athyridida is the Rostropiracea and the Spiriferinida is the Punctospiracea (suborders) of R.C, Moore in Moore, Lalicker, and Fischer, 1952.
Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rhynchonelliformea
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Virtual museum of the Czech Geological Survey, www.geology.cz, (C) Czech Geological Survey, 2011, v.0.99 [13.12.2011]

![[ENG]](img/vlajka-cr.gif) Česky
Česky 
 Previous
Previous